
22.May.2023
In this article, we will try to design an IoT system. We will set an example and look for the answer to the question of how we can make it an IoT system.
The name of this application, which we will design using the installed software on classical web servers, is “GPS tracking system”.
Apache.exe, MySQL.exe, Php.exe programs will be installed and running on our web server. As an example site, we determined the domainiot.milivolt.news.
The hardware and software components of the system will be as follows.
The schematic description of the system is below:
General schema
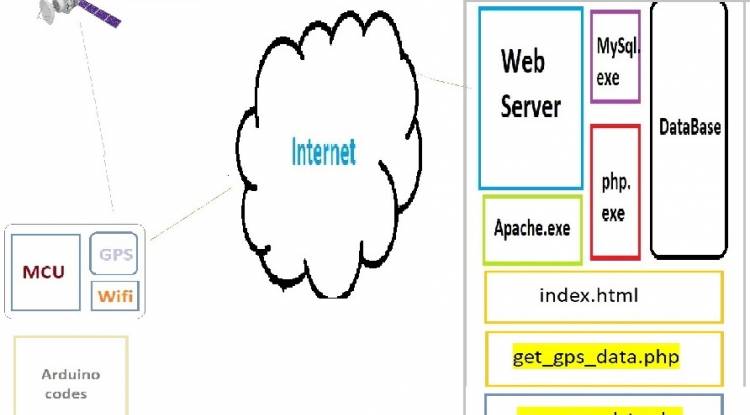
There are many alternatives as a microcontroller. But we assume that we will use Arduino Uno or Arduino Nano in this application.
Let's take a look at the microcontroller codes right away:
In order to be able to use these modules after the module connections are made to the system, we must first add the module libraries with the "#include" statement. As will be understood immediately, "TinyGPS++" will be used to operate with the GPS module, and "ESP8266Wifi" will be used to operate with the Wifi module.
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
// WiFi info
const char* ssid="your WIFI_SSID";
const char* password="your WIFI_PASSWORD";
// GPS pins
const int GPS_RX_PIN=2;
const int GPS_TX_PIN=3;
// GPS object
TinyGPSPlus gps;
// WiFi object
WiFiClient client;
// Iot.milivolt.News addrs.and port number (80, for http)
const char* server="iot.milivolt.news";
const int port=80;
void setup() {
// Serial baud rate
Serial.begin(9600);
// WiFi connect
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() !=WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(1000);
Serial.println("WiFi waiting...");
}
Serial.println("WiFi connected!");
}
void loop() {
// read data from GPS
while (Serial.available() > 0) {
if (gps.encode(Serial.read())) {
if (gps.location.isValid()) {
// GPS coord.
float latitude=gps.location.lat();
float longitude=gps.location.lng();
// send GPS data to server (iot.milivolt.news)
sendGPSData(latitude, longitude);
// 2 seconds wait
delay(2000);
}
}
}
}
void sendGPSData(float latitude, float longitude) {
// connect to server
if (client.connect(server, port)) {
// GPS data
String gpsData="latitude=" + String(latitude, 6) + "&longitude=" + String(longitude, 6);
// HTTP POST request
String postRequest="POST /save_gps_data.php HTTP/1.1\r\n";
postRequest +="Host: " + String(server) + "\r\n";
postRequest +="Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded\r\n";
postRequest +="Content-Length: " + String(gpsData.length()) + "\r\n";
postRequest +="Connection: close\r\n\r\n";
postRequest +=gpsData;
// POST to server
client.print(postRequest);
// Get response from server
while (client.connected()) {
if (client.available()) {
String response=client.readStringUntil('\r');
Serial.println(response);
}
}
// close port
client.stop();
} else {
Serial.println("Could not connect to server!");
}
}
After receiving the GPS data with the sendGPSData(float latitude, float longitude) line, it is sent to the server. On the server side, there should be a file with the extension "php" that receives these data. The name of this file is “save_gps_data.php”. These codes on the web server side are below:
On the web server side, a database must have been created before. We record two GPS data on our table with the registration codes of the database, the user name and password of which are specified.
<?php
// Enter the required information for the database connection
$servername="localhost";
$username="mysql_user";
$password="mysql_password";
$dbname="database_name";
// receive POST Data
$latitude=$_POST['latitude'];
$longitude=$_POST['longitude'];
// Connect to Database
$conn=new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Database connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
// record to GPS data
$sql="INSERT INTO gps_data (latitude, longitude) VALUES ('$latitude', '$longitude')";
if ($conn->query($sql)===TRUE) {
echo " GPS data saved successfully.";
} else {
echo "Error: " . $sql . "<br>" . $conn->error;
}
// Close the database connection
$conn->close();
?>
Due to the delay(2000) line we wrote in Arduino codes, these php extension codes will run every 2 seconds. The duration can be changed if desired.
Now it's time to display this GPS data on a map. For this, a file with the extension "html" is needed. In the html file below, there are JavaScript codes that pull the GPS data recorded in the database at certain time intervals. Let the name of this file be index.html.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="initial-scale=1.0">
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>GPS Data</title>
<style>
#map {
height: 400px;
width: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>GPS Data</h1>
<div id="map"></div>
<script>
function initMap() {
// Create a map
var map=new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById('map'), {
zoom: 15,
center: {lat: 0, lng: 0}
});
// get GPS data and marker
setInterval(function() {
fetchGPSData(map);
}, 2000);
}
function fetchGPSData(map) {
// get GPS data
fetch('http://iot.milivolt.news/get_gps_data.php')
.then(response=> response.json())
.then(data=> {
// Mark the GPS data on the map
var latitude=parseFloat(data.latitude);
var longitude=parseFloat(data.longitude);
var marker=new google.maps.Marker({
position: {lat: latitude, lng: longitude},
map: map
});
// Updates maps center
map.setCenter({lat: latitude, lng: longitude});
})
.catch(error=> {
console.log('Error:', error);
});
}
</script>
<script async defer
src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?key=YOUR_API_KEY&callback=initMap">
</script>
</body>
</html>
Among these codes, there is a "get_gps_data.php" that pulls the codes from the database in the background. These codes are below:
<?php
// Enter the required information for the database connection
$servername="localhost";
$username="mysql_user";
$password="mysql_password";
$dbname="database name";
// Connect to database
$conn=new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Database connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
// Get latest GPS data from database
$sql="SELECT latitude, longitude FROM gps_data ORDER BY id DESC LIMIT 1";
$result=$conn->query($sql);
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
// Get the latest recorded GPS data
$row=$result->fetch_assoc();
$latitude=$row["latitude"];
$longitude=$row["longitude"];
// Generate the JSON data
$data=array(
'latitude'=> $latitude,
'longitude'=> $longitude
);
// Send JSON data as output
header('Content-Type: application/json');
echo json_encode($data);
} else {
echo "GPS data not found.";
}
// close connect
$conn->close();
?>
Let's make an evaluation about the project design:
The microcontroller software receives the coordinate data via the GPS module and sends it to the iot.milivolt.news server via the WiFi module. The data coming to the server is saved to the database via “save_gps_data.php”.
The index.html file on the iot.milivolt.news site, on the other hand, visualizes the GPS data with the help of the javascript codes it contains.
The general structure and operation of our project will be like this. This project was designed for experimental purposes. Many features can be added to the project. For example, a membership system can be added so that many users can record and monitor their own tracking data.
In order for multiple IoT (MCU+Wifi+GPS) to be added to the system, a separate credential must also be given to each IoT object.
This tracking system can be used for different purposes depending on the type of things being tracked. If we are tracking motor vehicles, fuel consumption and fuel expenses can also be monitored using the recorded tracking data.

How to make a night light with Bluetooth control and three colors?
A practical and inexpensive night light design with Bluetooth control
03.03.2023

Measuring DC Volts with Android Phone - Voltmeter
Converting an old tablet computer to a voltmeter (with bluetooth)
04.03.2023

We make temperature and humidity detection system with Android device
Android apps
05.03.2023

A BlueTooth-controlled Android App to Measure Heart Rate
An application related to biomedical devices: Measuring heartbeats
08.03.2023
Controlling 8 LEDs with Android phone
Android apps with Bluetooth Module
13.03.2023
DC Motor Speed Control by Android phone
Android Mobil Apps
14.03.2023

Controlling multiple devices with Android phone
Android Apps with Bluetooth
15.03.2023

Projects with Wifi Module
Wifi module settings
20.03.2023
Application to Control Led Matrix Panel with Android Phone - Part 1
Led Panel-Bluetooth Apps
29.03.2023

Reading the Weather Using the GSM Module Connected to the Microcontroller
How to make weather reading application with GSM module
24.05.2023
Smart Homes Can Be Smarter Than Us.
I'm Programming My House.
18.12.2022

IoT impact in the Healthcare Industry
What is the level of applications of IoT objects in the health sector?
22.12.2022

Application of IoT(Internet of Things) Technologies to Animals
Animals on the Internet
23.12.2022

Smart Cars in the IoT Universe
The evolution of Smart Cars
24.12.2022

Use of HM-10, HC-06 and HC-05 Bluetooth Modules in IoT Projects
Use of HM-10, HC-06 and HC-05 Bluetooth Modules
23.01.2023
Led Control Application with HC-05 Bluetooth Module
Led Control with Android Phone-Flutter
25.02.2023

Electronic Organ Construction with HC-05 Bluetooth Module
Electronic organ design with the program written with Flutter-Dart codes
25.02.2023

220 Volt Lamp On-Off Application with Bluetooth
A bluetooth application made with Flutter-Dart codes
25.02.2023

Measuring resistance by phone to Android
Measuring resistance by phone to Android( with Flutter-Dart)
02.03.2023